How AI Road Inspections Can Support MIRE 2.1 Compliance and Improve Road Maintenance and Road Safety
- Maintain-AI
- Dec 15, 2024
- 15 min read
Transforming Road Asset Monitoring with Automated Inspections and Machine Learning Assessments

Key Takeaways:
While MIRE 2.1 was developed by the USA Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), its principles extend beyond American roads. Road agencies and infrastructure owners globally can adopt similar frameworks, underscoring that "A Safe Transport and Road System starts with quality data."
Data-Driven Safety Analysis (DDSA) is vital for making sound decisions regarding the safety, design and operation of roadways for all users. MIRE 2.1 reflects the evolution of federal safety data policy and the integration of national best practices, providing a model for consistent, actionable and integrated roadway data. Its adoption enables agencies to:
Develop a systematic approach to identifying safety needs.
Leverage advanced technologies, like AI, to enhance compliance and road asset monitoring.
Drive significant improvements in road safety assessments and infrastructure planning globally, reflecting the evolving demands of modern roadway networks.
Introduction - Artificial Intelligence is the Future of Road Asset Management
The Model Inventory of Roadway Elements (MIRE) 2.1 is a critical framework designed to enhance roadway safety through comprehensive, data-driven analysis. By standardising data collection for roadway attributes, MIRE 2.1 aims to improve traffic safety measures and support informed decision-making, paving (pardon the pun!) the way for safer and more efficient transportation networks. However, traditional data collection methods—reliant on manual inspections and inconsistent records—are time-intensive, expensive and prone to human error. These limitations make it challenging for agencies to achieve the level of precision and consistency required for effective safety analysis.
By turning roads into data and data into action, AI redefines safety—shifting from reactive measures to proactive precision for a safer tomorrow.
AI and computer vision technologies offer an innovative alternative, automating road inspections, and delivering a type of digital twin, that enables more efficient MIRE 2.1 data collection. These advanced tools significantly enhance data objectivity, consistency and timeliness, ensuring that critical roadway elements are captured without subjectivity.
Moreover, AI expands coverage to include previously neglected or hard-to-access areas, while reducing operational risks for on-site personnel. By adopting AI-powered road inspections, transportation agencies can transform their approach to MIRE 2.1 compliance, achieving improved safety outcomes, greater operational efficiency and cost savings on an unprecedented scale.
What is MIRE 2.1?
MIRE 2.1, or the Model Inventory of Roadway Elements, is a standardised framework developed to collect detailed roadway data. Its primary objective is to support data-driven safety analysis and enhance decision-making processes related to traffic safety and infrastructure management.
By categorising roadway features into six (6) primary groupings (Segments, Intersections, Intersection Legs, Interchanges/Ramps, Horizontal Curves and Vertical Grade) and encompassing over 200 sub-elements, MIRE 2.1 ensures that critical safety data is captured systematically. This structured approach aids transportation agencies in identifying high-risk areas, prioritising improvements and measuring the effectiveness of implemented safety measures.
Why is MIRE 2.1 Compliance Important?
Compliance with MIRE 2.1 is vital for transportation agencies aiming to improve roadway safety and meet federal requirements. Data-driven safety analysis (DDSA) is essential for making sound decisions on the safety, design and operations of roadways for all users. By leveraging MIRE 2.1’s structured framework, agencies can:
Enhance Roadway Safety: By identifying and addressing high-risk areas, agencies can reduce accidents and fatalities through targeted safety interventions. AI-enabled data provides a clearer understanding of crash-prone zones and potential hazards, enabling the implementation of effective countermeasures such as improved signage, road realignment or enhanced lighting.
Prioritise Investments: Efficiently allocate resources to the most critical safety needs by leveraging detailed and timely data analytics. AI-driven insights enable agencies to rank projects based on urgency, cost-benefit analysis and potential impact on roadway safety, ensuring optimal use of limited funds.
Meet Federal Standards: Access funding and support by adhering to standardised data collection processes. Meeting MIRE 2.1 requirements allows agencies to qualify for federal grants and compliance incentives, ensuring that infrastructure improvements are not only funded but also aligned with national safety goals. In addition, this compliance streamlines inter-agency collaboration and reporting by providing a uniform framework for data exchange.
How Does AI Improve MIRE 2.1 Data Collection?
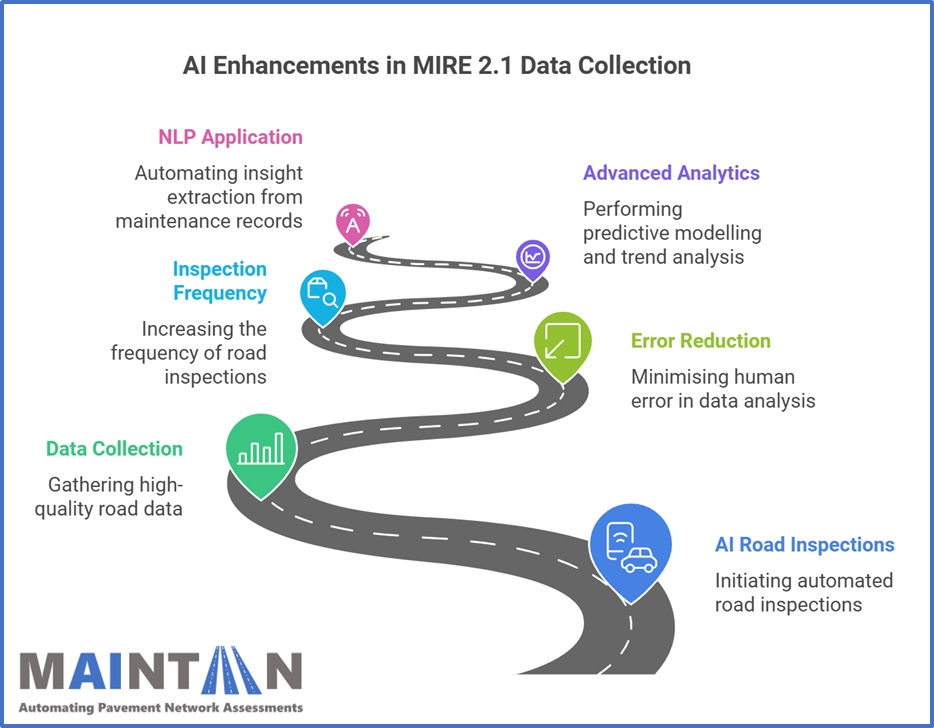
AI technologies, such as AI road inspections, significantly enhance MIRE 2.1 data collection by automating road condition inspections and providing consistent, near real-time insights. Through machine learning and computer vision, AI can:
Collect high-quality data more efficiently than traditional methods, including detailed attributes like lane widths, pavement health conditions and traffic sign inventories.
Reduce the risk of human error in identifying roadway elements by providing objective, automated analysis.
Improve the frequency and coverage of inspections, ensuring that all critical areas are assessed consistently, including remote and hard-to-reach locations.
Enable advanced analytics such as predictive modelling and trend analysis to proactively address safety and maintenance issues before they escalate.
Beyond machine learning, other AI technologies like natural language processing (NLP) and decision intelligence can enhance MIRE 2.1 compliance. For instance, NLP can automate the extraction of insights from road maintenance records, while decision intelligence can simulate and optimise roadway improvement strategies. Additionally, sensor fusion techniques can integrate data from LiDAR, cameras and IoT devices, improving the accuracy of detecting features like vertical grade and interchange geometry.
MIRE 2.1 Data Elements and AI Applicability
MIRE 2.1’s diverse data requirements present a unique opportunity to leverage AI technologies for improving roadway safety. By systematically organising roadway attributes into distinct groupings, MIRE 2.1 enables a structured approach to identifying safety needs and implementing targeted solutions. AI's ability to automate and enhance data collection makes it a transformative tool for addressing these requirements, ensuring transportation agencies can meet compliance standards while improving efficiency and accuracy.
MIRE 2.1 comprises six (6) primary data type groupings, each requiring detailed collection and analysis:
Segments: Roadway classification, surface type and median characteristics.
Intersections: Geometry, traffic control devices and safety features.
Intersection Legs: Attributes of connecting roadways.
Interchanges / Ramps: Ramp configurations and merging zones.
Horizontal Curves: Curve radii, superelevation and alignment.
Vertical Grade: Road elevation changes and gradient characteristics.
AI Applicability to MIRE 2.1 Elements
AI technologies demonstrate varying degrees of applicability to MIRE 2.1 elements. By aligning these capabilities with the data requirements of MIRE 2.1, transportation agencies can unlock unprecedented efficiencies in road safety analysis and infrastructure management. From mapping intersections to assessing pavement conditions, AI offers tailored solutions that target specific roadway characteristics. The ability to automate data collection and analysis brings transformative potential to compliance efforts, ensuring a high breadth of data and consistency across vast transportation networks.
High Potential:
Pavement Condition: AI can assess surface type, detect cracks, potholes and measure serviceability ratings (PSR).
Lane and Shoulder Markings: Computer vision can evaluate lane widths, shoulder dimensions and identify bicycle facilities or rumble strips.
Traffic Control Devices: Object detection algorithms can inventory signs and signals while assessing their condition.
Intersection Geometry: AI tools map complex intersections and ramps with high accuracy.
Moderate Potential:
Horizontal Curves: While achievable, detecting subtle curve characteristics may require specialised LiDAR data.
Vertical Grade: Gradient analysis is feasible but may demand advanced modelling tools.
Lesser Potential:
Rare attributes like Horizontal Curve Intersection / Deflection Angle and Curve Superelevation are less suited for AI-driven approaches.
By focusing on high-potential elements, agencies can leverage AI to achieve comprehensive MIRE 2.1 compliance, addressing the most impactful roadway characteristics.

AI Powered Road Inspection Technologies and Methods to Support Improved Road Infrastructure Management and Road Safety
As the complexity and size of roadway systems grows, the need for advanced tools to support efficient and objective inspections becomes even more critical. AI-powered technologies provide a transformative approach to road inspections, leveraging data acquisition, processing and analytical capabilities to streamline the collection and analysis of MIRE 2.1 elements. These technologies not only enhance data quality but also enable proactive roadway management, setting a new standard for transportation agencies.
Core Technologies Enabling AI Road Inspections
Effective AI-driven road inspection systems rely on a combination of advanced technologies that enable scalable and efficient data collection and analysis. These foundational technologies work together to address the diverse requirements of MIRE 2.1 while improving overall infrastructure management.
Data Acquisition:
Mobile LiDAR: Provides precise, three-dimensional mapping of roadway features, such as surface conditions and markings. While highly accurate, LiDAR technologies are expensive, often provide more detail than needed for most decision making and are best utilised as supporting solutions alongside other cost-effective approaches. Their cost prohibits frequent use, conflicting with the fundamental need for regular data collection to drive transformative improvements in recurring road infrastructure strategies.
High-Resolution Imagery: Captures detailed visual data from cameras, offering a more accessible and scalable option for roadway analysis. Modern camera technologies provide extensive coverage, offering a cost-effective alternative to systems like LiDAR. Although they may not achieve the same level of accuracy, the data they generate plays a crucial role in supporting more informed and timely maintenance decisions. This includes identifying road surface defects and monitoring infrastructure conditions, making them an invaluable tool for road asset management.
Drones and Sensors: Provide cost-effective methods for inspecting hard-to-reach areas. Equipped with imaging capabilities, drones efficiently cover challenging terrains, capturing high-resolution data on road conditions. Sensors tailored to specific needs, such as thermal imaging for pavement temperature or infrared for structural weaknesses, enhance accessibility and targeted assessments.
2. Computer Vision and Machine Learning:
Object Detection Models: Recognise traffic signs, pavement markings and numerous types of road defects. These models can also assess the presence and visibility of critical signage in varying weather and lighting conditions, ensuring road safety elements are consistently monitored.
Image Classification and Semantic Segmentation: Extract features such as lane boundaries and shoulder widths. These techniques are also capable of identifying faded or damaged pavement markings and distinguishing between different types of road markings (e.g., bike lanes, pedestrian crossings and lane dividers).
Instance Segmentation: Goes beyond semantic segmentation to identify individual objects on the roadway, such as vehicles, barriers and debris, enabling more granular data collection.
Feature Tracking: Monitors dynamic elements, such as vehicle movement or pedestrian activity, to provide insights into traffic flow and potential safety hazards.
3. Data Processing and Management:
Cloud computing supports large-scale data processing and storage, enabling real-time workflows and cross-agency collaboration. It provides the scalability needed to handle massive datasets generated by AI-powered inspections, allowing agencies to analyse and share data seamlessly across platforms. Advanced cloud solutions also offer automated backup systems and data recovery options, ensuring critical information is always secure and accessible.
Key AI Inspection Methods
AI inspection methods offer innovative approaches to assessing road infrastructure, addressing critical safety and maintenance challenges with greater precision and efficiency.
Automated Pavement Distress Analysis: AI detects surface defects like cracks, potholes and rutting, delivering detailed condition assessments. Advanced computer vision models can differentiate between types of cracks (e.g., transverse, longitudinal) and classify their severity, enabling targeted maintenance strategies. Additionally, these systems can attempt to predict future pavement deterioration trends based on historical data, improving long-term infrastructure planning.
Sign Inventory and Condition Assessment: Algorithms identify missing or damaged signs, enhancing traffic control device records. AI tools can also assess sign visibility and retroreflectivity under varying conditions, such as nighttime or adverse weather, ensuring compliance with safety standards. Furthermore, automated systems can detect unauthorised signage or obstructions, maintaining regulatory compliance.
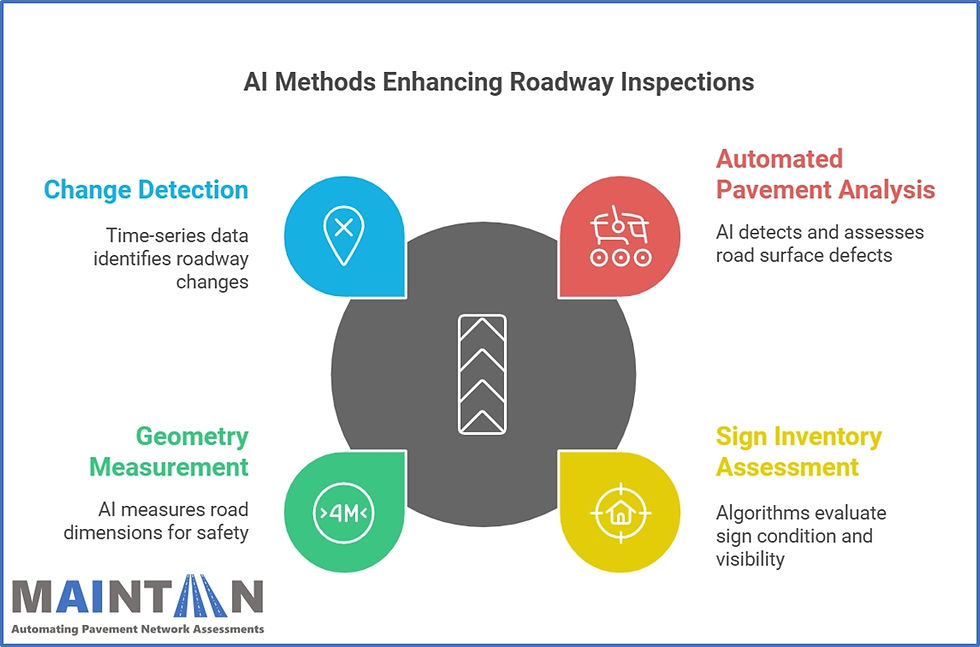
Roadway Geometry Measurement: AI extracts dimensions of lanes, shoulders and clear zones, streamlining geometric analysis. AI can also analyse cross slopes, super-elevations and other complex geometric attributes, supporting advanced roadway design and safety evaluations.
Change Detection: Using time-series data, AI highlights alterations in roadway features, enabling proactive maintenance planning. These systems can detect subtle shifts, such as minor surface deformation or vegetation encroachment, before they escalate into significant issues. Advanced algorithms also compare historical and current data to identify trends, helping agencies allocate resources effectively for preventive measures.
AI technologies are reshaping how roadway inspections are conducted, offering tools that not only address immediate compliance needs but also directly support the data objectivity and comprehensiveness required by MIRE 2.1. By integrating diverse data acquisition methods with powerful processing capabilities, agencies can ensure that critical elements like intersection geometry, pavement conditions and traffic control devices are systematically captured.
This modernised approach enhances the ability to address MIRE 2.1’s multifaceted requirements while fostering more responsive and dynamic transportation networks.
Benefits of AI Road Inspections for MIRE 2.1 Compliance and Understanding Road Condition Information
AI-powered road inspections are transforming the way transportation agencies achieve MIRE 2.1 compliance. By replacing manual processes with automated systems, AI enhances data timeliness and consistency while reducing operational risks and costs. These benefits address the core challenges of traditional methods, enabling a more comprehensive and proactive approach to roadway safety.
This shift represents not just a technological upgrade but a fundamental change in how agencies approach roadway safety and infrastructure management. With AI enabling consistent and objective data collection at scale, transportation networks can be managed more effectively, ensuring resources are allocated where they are needed most.
1. Improved Data Objectivity:
Automated tools eliminate subjective biases, providing consistent and detailed measurements. By removing the variability introduced by human inspectors, AI ensures that data on roadway attributes like lane markings, sign inventories and pavement conditions remains reliable over time. This level of objectivity is essential for detecting trends and implementing safety measures effectively.
2. Enhanced Timeliness:
AI enables faster data collection, allowing more frequent updates and real-time insights. Instead of weeks or months of manual inspections, AI systems can process data in hours or even minutes, enabling agencies to make timely decisions on roadway maintenance and safety interventions.
3. Increased Coverage:
Cost-effective scalability ensures comprehensive inspections across extensive networks, including remote areas. AI technologies can be deployed on vehicles, drones or fixed installations to cover vast regions, identifying and assessing even the most inaccessible road segments with minimal resource requirements.
4. Reduced Costs:
Automation reduces reliance on labour-intensive fieldwork, driving down overall expenses. By eliminating the need for large inspection crews, agencies can allocate budgets more efficiently toward critical infrastructure improvements and safety initiatives.
5. Improved Safety:
By minimising on-site personnel requirements, AI reduces risks associated with roadside inspections. The integration of automated tools ensures that inspections are carried out without exposing staff to hazards like heavy traffic or dangerous terrain, significantly lowering the risk of workplace accidents.
6. Seamless Data Integration:
AI-derived datasets integrate seamlessly with existing systems, enriching overall safety analysis. These systems allow for direct connections with Geographic Information Systems (GIS), traffic management software, and predictive analytics platforms, ensuring that the data collected can be utilised immediately for decision-making and planning purposes.
Automated systems supported by ai algorithms can now enable frequent and detailed inspections of a broader range of road infrastructure, providing actionable insights without exposing staff to hazards like heavy traffic or dangerous terrain. This expanded capability allows agencies to collect and analyse a more comprehensive set of data, significantly enhancing the assessment of infrastructure elements and driving improved safety outcomes across the entire transportation network.
The adoption of AI in road surface and road condition inspections across all road networks will represent a pivotal step toward fulfilling MIRE 2.1 requirements more efficiently. By embracing these technologies, road authorities can ensure comprehensive, objective and cost-effective data collection, fundamentally shifting how roadway safety and maintenance are managed for long-term benefits.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies of AI-Driven Road Inspections to Support MIRE 2.1 (and how Maintain-AI helps)
The integration of AI in road inspections delivers immense potential but is not without its challenges. Agencies must navigate obstacles ranging from data requirements to computational demands to fully harness AI’s capabilities. Understanding these barriers and implementing robust solutions is critical for ensuring the success of AI-powered inspections. Maintain-AI provides targeted strategies to overcome these hurdles, empowering agencies to confidently adopt and scale AI technologies for roadway management.
Key Challenges Maintain-AI’s Solutions' Solve
Data Requirements: Maintain-AI’s curated dataset accelerates model development, offering diverse road images and conditions to enhance AI consistency. This approach not only reduces the burden on agencies to train their own data but also ensures that the AI models are exposed to a wide variety of road types, climates and traffic scenarios, improving their robustness and generalisability. By continuously expanding its dataset with new inputs, Maintain-AI enables systems to adapt to evolving infrastructure needs.
Computational Resources: Maintain-AI's cloud-based platform provides scalable infrastructure, eliminating the need for costly hardware investments. This scalability ensures that even agencies with limited resources can process and analyse large datasets efficiently.
Algorithm Development and Validation: Maintain-AI’s expert team continuously refines algorithms, ensuring reliable performance across various road features. Through rigorous testing, including cross-validation with multiple datasets and environmental conditions, Maintain-AI ensures that its algorithms deliver consistent and accurate results. This iterative development process accounts for edge cases, such as extreme weather or unusual road configurations, to maximise reliability.
We acknowledge that no system can deliver 100% accuracy, as perfection is unattainable despite claims contrary by some. However, with each use, our platform significantly enhances your understanding of road networks, enabling more informed decisions and driving continuous improvements in road infrastructure management.
Scalability and Implementation Challenges: Adopting AI solutions often requires significant upfront investments in technology and training, which can be challenging for agencies with limited budgets or resources. Maintain-AI mitigates this by offering modular, scalable solutions that allow agencies to start small and expand their capabilities over time. Through customised implementation plans and ongoing technical support, Maintain-AI ensures that agencies can integrate the data we provide at their own pace without compromising operational efficiency or effectiveness.
By addressing these challenges, Maintain-AI empowers agencies to harness AI’s growing potential, making MIRE 2.1 compliance accessible and practical. Beyond immediate compliance, this approach fosters a proactive and scalable model for roadway management, enabling agencies to continuously adapt to evolving infrastructure needs. With advanced AI tools and support systems, transportation networks can be managed with greater precision, efficiency and safety, driving long-term improvements across diverse environments.
Future Directions - AI and Machine Learning Pivoting MIRE 2.1 Through Road Intelligence
AI and computer vision technologies are advancing rapidly, offering a suite of capabilities that align directly with MIRE 2.1’s expansive requirements. Enhanced object recognition systems are now capable of identifying and assessing critical infrastructure components such as lane markings, barriers and road surface conditions with unprecedented precision. Real-time data analysis is enabling transportation agencies to detect patterns and anomalies faster than ever, facilitating quicker interventions for potential safety hazards.
Emerging predictive maintenance strategies leveraging AI are continually evolving to forecast potential infrastructure degradation and prioritise associated risks based on their projected impact. Although still evolving, these advancements have the potential to help agencies allocate resources more effectively, enhancing infrastructure resilience and overall safety. Additionally, advancements in sensor integration and multi-modal data collection are expanding the scope of what can be measured, such as improved geometric assessments of intersections and ramps, providing actionable insights that were previously unattainable through traditional methods.
AI isn't just helping us see roads differently; it's enabling us to predict, prioritise and proactively reshape the future of infrastructure safety.
Maintain-AI showcases how emerging technologies can transform road maintenance by combining advanced AI systems with practical strategies tailored to meet the unique needs of transportation agencies. By bridging the gap between traditional methods and innovative, data-driven approaches, Maintain-AI makes adopting AI technologies both achievable and essential for modern infrastructure management. Addressing key challenges such as scalability, and efficient resource use, Maintain-AI provides agencies with the tools to improve their road maintenance strategies and adapt to evolving demands in infrastructure management and the requirements of MIRE 2.1 compliance.
As transportation agencies continue their journey toward full MIRE 2.1 compliance, sustained investment in research, development and validation of AI methods will be crucial. The potential of AI to revolutionise road safety resides in its ability to adapt and scale with changing infrastructure demands, ensuring that agencies are always equipped to meet evolving challenges. By embracing these technologies, agencies can move beyond compliance to achieve a proactive, predictive, and highly efficient approach to safety management—creating smarter, safer and more sustainable road networks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Question 1: How does AI-driven inspection systems improve the detection of road damage and road defects in comparison to traditional inspection methods as outlined in MIRE 2.1?
Road AI driven inspection solutions significantly enhance the assessment of road conditions and the detection of road damage and defects by automating the analysis of roadway images and geospatial data, reducing reliance on traditional manual surveys.
MIRE 2.1 emphasises the need for detailed roadway and traffic inventories, which AI can achieve by leveraging advanced machine learning models like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for defect detection. This includes identifying cracks, potholes, and wear patterns on road and pavement surfaces. These systems can analyse large-scale imagery datasets to provide more holistic and timely assessments compared to labour-intensive traditional methods.
By accelerating the inspection process, AI reduces life-cycle costs and minimises errors, allowing better management of road lifecycles and resource allocation.
Question 2: How can AI-driven inspection systems improve lifecycle management and cost-effectiveness in managing road highway maintenance, as envisioned in MIRE 2.1?
AI-driven inspection systems enhance lifecycle management by enabling proactive maintenance strategies. MIRE 2.1 focuses on comprehensive data collection to assess road conditions. AI supports this goal by continuously monitoring and analysing metrics such as pavement quality, road usage, and defect severity.
With the potential for predictive analytics, AI helps forecast the progression of damage and prioritises interventions to prevent costly failures. For highways, this reduces the economic burden of reactive repairs and prolongs the infrastructure lifecycle.
AI-based systems integrate seamlessly with data collection provisions in MIRE 2.1, such as using imagery and geospatial tools, ensuring consistent and high-quality data across various types of road networks. This improves decision-making and allocates resources more effectively, yielding significant cost reductions.
Question 3: How does the integration of AI into MIRE 2.1 data collection standards support better road user safety and improve the overall inspection process or roads and pavement and associated infrastructure?
AI integration aligns with MIRE 2.1's emphasis on data-driven safety enhancements by improving road defect detection, which is critical for road user safety. Traditional inspection methods often miss subtle defects or require significant time to report findings, delaying necessary interventions.
AI-driven systems use visual inspection analysers and advanced algorithms to detect road defects like potholes, cracks, and surface wear in real-time. These systems allow road agencies to quickly address hazardous conditions, reducing the risk of accidents.
Furthermore, AI for roads enables the classification of various types of road damage by severity and urgency, aligning with MIRE’s framework to manage metrics for road safety. This ensures a safer experience for road users while optimising the inspection process for economic and operational efficiency.
Maintain-AI is on a journey to support road authorities make more informed decisions but we only have some of the solutions. Let's work together.
Remember, good roads should cost less.
Let us know your thoughts?
Drive safely;
About Maintain-AI:
Maintain-AI aspires to support Governments, other Road Asset owners and Industry professionals transform pavement and network assessments through AI-driven solutions. Founded on the principle that "Good Roads Should Cost Less", we harness the power of computer vision and machine learning to automate road surface inspections. Our state-of-the-art tools detect road defects and assess related infrastructure, enabling professionals to make data-driven decisions. By advocating for the optimal use of maintenance budgets, we emphasise that well-maintained roads are more cost-effective across a road's complete asset lifecycle. Our commitment is to support regular, objective network inspections, ensuring that every maintenance dollar is maximised. With Maintain-AI, infrastructure asset management is not only efficient but also offers a clear return on investment through maintenance savings. Join us in our mission to make roads better, safer, more sustainable and more cost-effective. All road users deserve it.
AI Road Inspections
MIRE 2.1 Compliance
Road Safety Analysis
Data-Driven Infrastructure
Automated Pavement Analysis
Predictive Road Maintenance
AI for Road Management
Transportation Data Collection
Smart Infrastructure Solutions
Computer Vision Road Inspections
Big Data in Transportation
Traffic Analytics Technology
Connected Vehicles
V2V
Smart City Infrastructure
IoT and Road Safety
Predictive Analytics in Transit
Sustainable Transportation Solutions
Digital Road Inspections
Digital Asset Management
Digital Transformation
Road AI
Maintain-AI
